The main goal of the lab is the study and the development of fluid automation components and their itegration into systems.
Here follows a short description of the activities of the laboratory sorted by the main interest areas.
|
|
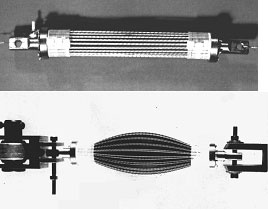
Straight fibres pneumatic muscle
Carlo Ferraresi; Walter Franco; Andrea Manuello Bertetto
An evolution of the McKibben muscle.
The longitudinal orientation of the fibres gives particularly high force performance.
|
|
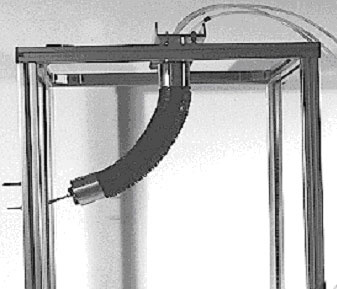
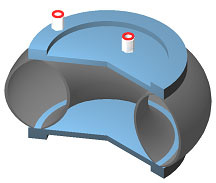
Proboscis actuator
Carlo Ferraresi; Andrea Manuello Bertetto, Gustavo Belforte, Francesco Pescarmona
Deformable fluid actuator. The internal section with 2 or 3 lobes allows bending in plane or space, controllable by the internal pressure.
|
|
|
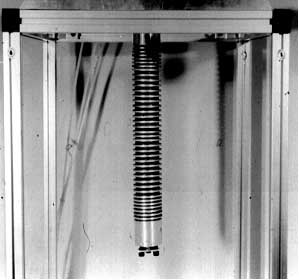
Deformable actuator BiFAc2
Carlo Ferraresi; Walter Franco; Giuseppe Quaglia
Deformable fluid actuator, able to exert both tensile and pulling forces, thanks to its structure with two co-axial membranes.
|
|
Deformable actuator BiFAc3
Carlo Ferraresi; Walter Franco; Giuseppe Quaglia
Its structure with three membranes allows, with respect to BiFAc2, greater possibility of configuration and, therefore, the use in applications as vibration control or development of vehicular semi-active suspensions.
|
|

|

|
|
|
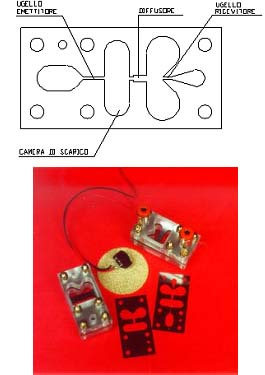
Laminar-turbulent amplifier
Guido Belforte; Gabriella Eula; Carlo Ferraresi; Vladimir Viktorov; Carmen Visconte
Digital interface between electric and pneumatic signals. Dimensions are small and electric consumption low. The main working principle is the transition of supply jet from laminar to turbulent field. There are an emitter nozzle and a receiver nozzle. The start of an acoustic signal between these two nozzles causes the laminar-turbulent supply jet transition. In this way the pressure recovered on output ports drastically drops. A variation of supply pressure about 30% do not disturb the interface behaviour. The results obtained are good and show the effective possibility to use this interface as pilot stage of pneumatic valves.
|
|
|
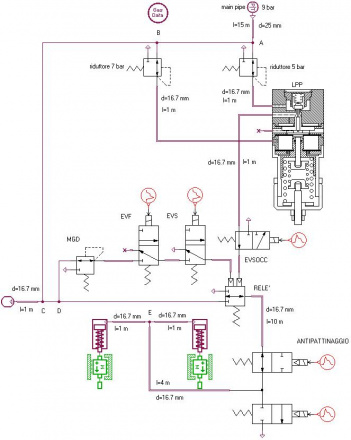
Braking systems for train and tram
Guido Belforte; Massimiliana Carello; Carlo Ferraresi ; Alexandre Ivanov; Matteo Martinelli; Francesco Pescarmona; Vladimir Viktorov
Modelling of pneumatic circuits for braking system using AMESim® program and experimental validation.
Collaboration:
Faiveley Transport S.p.A.
|
|
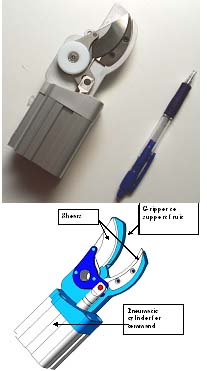
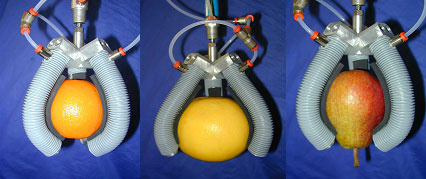
Hand with flexible fingers
Massimiliana Carello; Carlo Ferraresi; Carmen Visconte
Three pneumatically actuated fingers, having good adaptability in grasping various shape and size fruits, allow a quite uniform force distribution on the contact surface.
|
|
|
|

|
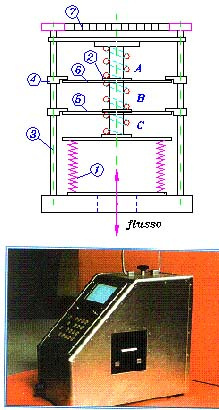
Tests on pneumatic components
Guido Belforte; Massimiliana Carello; Alexandre Ivanov; Matteo Martinelli; Francesco Pescarmona
Test rigs to measure the air-flow and the shifting time. They follow the latest ISO standard reference and are automatic, flexible, sensorized.
It is possible to test: pneumatic valves, air conditioning units, pneumatic components.
Maximum upstream pressure 12 bar ; air-flow range 200÷12000 dm3/min (ANR).
|
|
|
Tester for artificial ventilators
Guido Belforte; Gabriella Eula; Terenziano Raparelli
The test of artificial ventilators is obtained by means of tester machines. They can measure every patient pulmonary parameter, such as: anaesthetic gas mix; maximum and minimum pressure; inspiration/expiration ratio; pulmonary frequency.
Artificial lung models were realised, both with fixed and with variables pulmonary volumes. In this case, a bellows allows to simulate with a single device every patient condition (adult; child, infant).
|
|
|
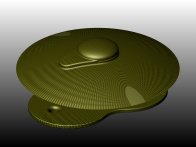
Phonatory VALVES
Guido Belforte; Massimiliana Carello
“in vitro” characterizations of phonatory valves, commercial and new prototype. In particular: direct and reverse air-flow measure, simulation of “real-working” (opening/closing) in “real” conditions
Collaborations:
ASO Ordine Mauriziano Presidio Ospedaliero Umberto I – Divisione O.R.L.
A.S.L. TO3 - Ospedali Riuniti di Pinerolo – Divisione O.R.L.
|
|
|
Visualisation techniques
Guido Belforte; Massimiliana Carello; Gabriella Eula; Carlo Ferraresi
To study fluidic and pneumatic components, visualisation techniques can be used. They are based on: fluid stream of hydrogen bubbles; coloured water stream; particles inside a fluid or on its surface.
For example, visualisation with hydrogen bubbles is realised by electrodes put inside a water stream. This technique was applied in various research, such as: study of velocity profile in fluidic amplifiers; study of vortex valves; study and optimization of fluid sealings for supply carburant in automotive field.
|
|
|
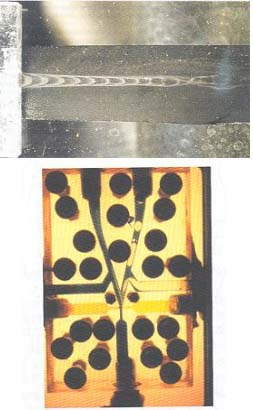
Oil filters
Guido Belforte; Terenziano Raparelli; Andrea Trivella
A test bench was organized to study the performance of air- oil coalescent filters. It allows the measure of the efficiency of the filters versus the air velocity, the operative pressure and the concentration of the injected oil.
The influence on efficiency of the type of the filtering media and the supply system of the cleaner body are studied. The figures show the scheme of the test bench, a filtering element with glass fibres and an enlargement, a cleaner body with transparent cup to visualize the coalescence.
|
|
|
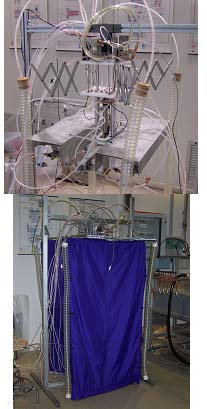
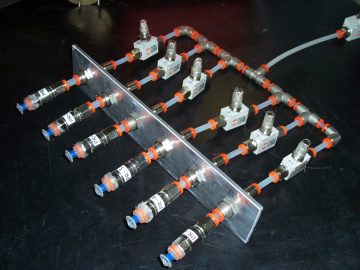
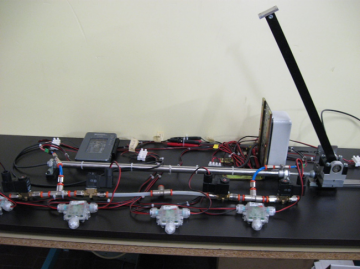
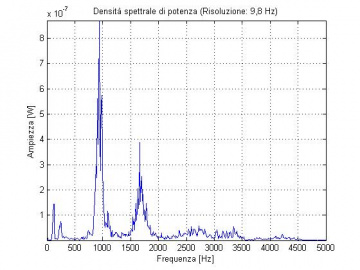
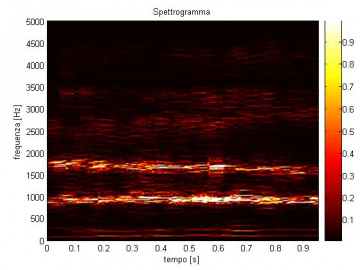
Pneumatically actuated inverted pendulum
A Pneumatically actuated inverted pendulum controlled with PWM modulated digital valves has been developed. A PLC or alternatively an Arduino board are used to control the system. The picture shows the test bench.
|
|
|
Voice analysis
Carello Massimiliana
Voice analisys (fundamental frequency, jitter, shimmer, maximum phonation time, ecc) of no-laringeal voice patients (oesophageal voice and voice with phonatory valve).
Collaborations:
ASO Ordine Mauriziano Presidio Ospedaliero Umberto I – Divisione O.R.L.
A.S.L. TO3 - Ospedali Riuniti di Pinerolo – Divisione O.R.L.
|
|

|
Artificial ventilators
Guido Belforte; Gabriella Eula; Terenziano Raparelli
Various kinds of prototypes of pneumatic ventilators were realised, using also electronic flow regulations.
In particular, they can be applied: for reanimation; for assisted ventilation; for pulmonary therapy; for anaesthesia.
|
|
|
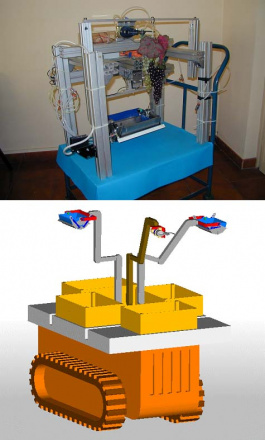
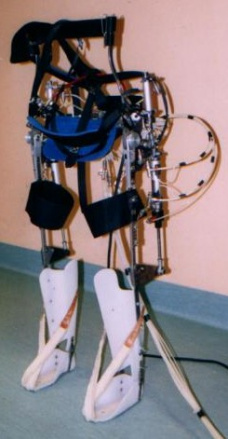
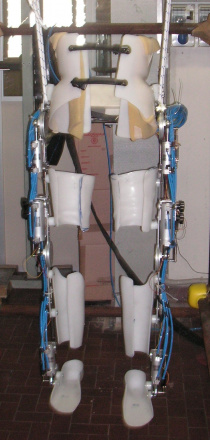
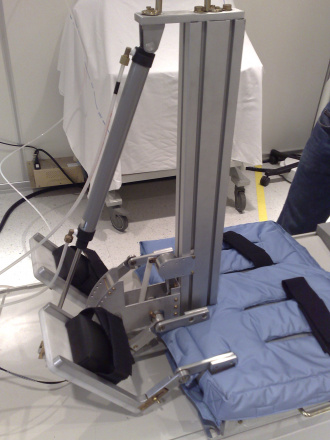
Active orthesis for gait rehabilitation
Silvia Appendino ; Guido Belforte; Gabriella Eula
The use of active orthesis allows rehabilitation of people with no mobility. The prototype currently in testing (P.I.G.R.O.) is adaptable to different anthropometric sizes and imposed gait pattern can be amended as needed. It allows the activation of hip, knee and ankle. The research is carried out in collaboration with doctors and health personnel and its aim is the development of a new rehabilitation approach.
Cooperation with Italian Puzzle Cooperative, University of Turin – Psychology Faculty – Koelliker Hospital and Santa Croce Hospital (Turin).
Founded by “Compagnia di San Paolo” in the project titled “Exoskeleton for functional rehabilitation in paretic patients mobility” and from country Piedmont (Italy) in the project titled: “Validation of a method for gait rehabilitation in paretic patients using an active orthosis”
|
|
|
Aid for controlled foot motion during fMRI
Silvia Appendino ; Guido Belforte; Gabriella Eula
The effectiveness of neuro-rehabilitation can be assessed through in vivo tests such as fMRI performed before and after treatment. To highlight the actual neurological changes examinations should be carried out under the same conditions. The developed, entirely non-magnetic device, imposes a periodic and controlled movement to the ankle joint. This permits to evaluate whether the reactivation of motor areas related to locomotion has occurred following rehabilitation.
Cooperation with Italian Puzzle Cooperative, University of Turin – Psicolocy Faculty – Koelliker Hospital and Santa Croce Hospital (Turin).
Founded by “Compagnia di San Paolo” in the project titled “Exoskeleton for functional rehabilitation in paretic patients mobility” and from country Piemonte (Italy) in the project titled: “Validation of a method for gait rehabilitation in paretic patients using an active orthesis”.
|
|

|
Winding
Guido Belforte; Alexandre Ivanov; Daniela Maffiodo; Francantonio Testore
The winding process of elastic yarns was optimised.
A parametric analysis was experimentally carried out by means of suitably designed test benches. In particular, the influence of the winding tension and of the angle of winding were analysed.
|
|
|
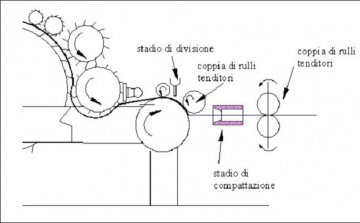
Carding
Guido Belforte; Alexandre Ivanov; Stefano Mauro; Francantonio Testore
A pneumatic device for carding allows avoiding the use of tape condenser with endless tape and of rubbing aprons.
|
|
|
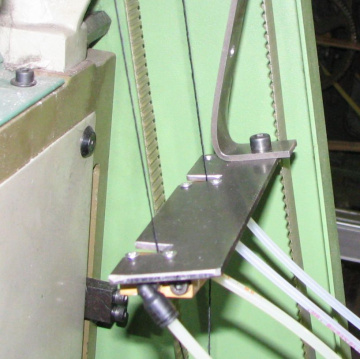
Slubbing devices
Guido Belforte; Alexandre Ivanov; Francantonio Testore
A device was developed to improve the compactness of the roving for combed fibres.
Experimental tests pointed out a more uniform behaviour, in terms of resistance, of the treated roving than that of the standard roving.
.
|
|

|
Raising
Guido Belforte; Gabriella Eula; Carlo Ferraresi; Alexandre Ivanov
An innovative process was developed aimed at finishing high quality wool fabrics. In particular, the raising phase was optimised, replacing standard teasels, made up of natural cards, by new metal teeth, able to reproduce the same effect.
Metal teeth with various geometries were manufactured and tested, able to produce fabrics with the same quality level as the standard ones, with the advantage of a longer life than the natural teasels.
|
|

|
Interlacing
Guido Belforte; Alexandre Ivanov; Stefano Mauro; Francantonio Testore
Interaction between the textile yarn and an air jet is provided inside a suitably designed chamber. The yarn fibres are initially spread and then strongly twisted.
The chamber geometry and the air flow-rate were chosen to ensure a periodic process: the yarn is made up of a sequence of compact parts (knots) and spread parts. The product quality depends, in fact, on both the knots regularity and on their internal friction.
Research is now focused on reducing air consumption.
|
|
|
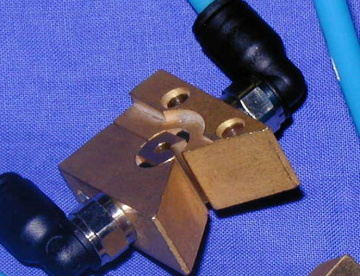
Reduction of yarn hairiness
Guido Belforte; Alexandre Ivanov; Matteo Martinelli
Terenziano Raparelli; Francantonio Testore;
Andrea Trivella; Vladimir Viktorov
A pneumatic device reduces the yarn hairiness, improving the fabrics quality.
An air vortex, generated around the yarn moving from the spindle to the reel, winds the hairiness and makes the yarn compact.
|
|
|
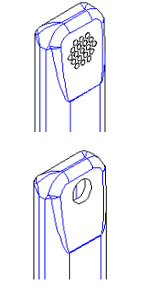
Air-jet loom auxiliary nozzles
Guido Belforte; Giuliana Mattiazzo; Vladimir Viktorov; Carmen Visconte
The airflow from sub- nozzles having different shapes was analysed. Some tests were carried out outside the profiled reed and comparison between nozzles was made in terms of air velocity distribution, jet spreading and consumption.
In order to analyse the interaction between the jet emitted by an auxiliary nozzle and the loom profiled reed, some velocity measurements were repeated inside the weft passage, at various distances from the nozzle exit.
|
|
|
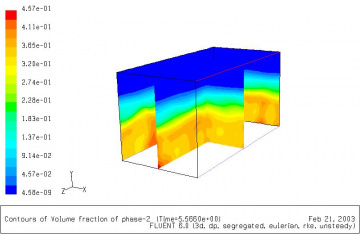
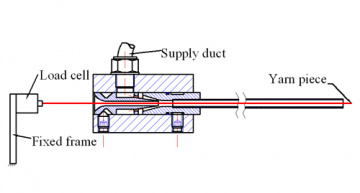
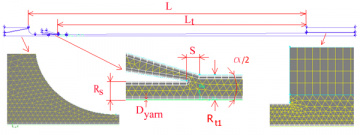
Air-jet loom main nozzle
Guido Belforte; Giuliana Mattiazzo; Vladimir Viktorov; Carmen Visconte
The drag force exerted by the main nozzle airflow in air-jet looms was studied, evaluating the influence of nozzle geometry and yarn material. In particular, length, shape and size of the acceleration tube were analysed.
Experimental tests were carried out on prototypes and numerical simulations were performed on a two-dimensional model implemented in the commercial CFD code Fluent.
|
|
|
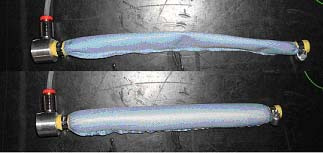
Pneumatic Muscles and Active Garments
Silvia Appendino; Guido Belforte; Gabriella Eula; Roberto Grassi; Alexandre Ivanov
Design and construction of pneumatic muscles with different joining technologies for their integration in active garments.
Project financed in PROGETTO MULTIREGIONALE HI-TEX Reg. Piemonte - D.G.R. n. 227-4715 del 27/11/2006
|